Variability
It is common in domain modeling and domain engineering to focus on narrow domains. This helps to avoid scope creep and exploit commonality. Managing **variability* is the price we have to pay for being able to support more than one product, but we want to keep the variability possible low (as a cost).
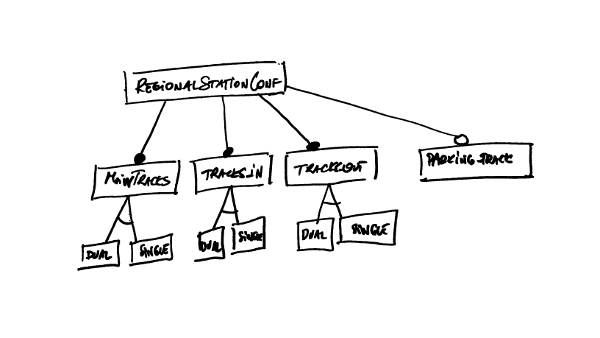
In this tutorial, we will concentrate our model on small regional stations. We scope our model to:
- allow single or dual main tracks,
- one or two input tracks,
- and one or two output tracks.
Finally, we observe that some stations (and only some) also have a side track, also known as a parking track, were trains can be stopped for longer periods.
Let’s reflect these changes in our feature model:
A few observations about this model
Recall that the symbol
?is a handy notation for0..1cardinality and we will use it from now onwards. This cardinality represents optional features, so this is one way we introduce variability in the model.Cardinality constraints that are written to the left of the clafer name restrict the cardinality of the set of all children. We call such a cardinality constraint a group cardinality (as opposed to clafer cardinality)
xoris a shortcut for1..1again, but traditionally used for group cardinality describing a choice of an alternative. It means that only one of the children can be selected at a time. Think of this group as ‘Radio Buttons’.other useful group cardinalities include
mux(which stands for0..1), andor(which stands for1..*). The former means that at most one sub-clafer can be instantiated, but perhaps none. This is a classic mutual exclusion requirement (an exclusion group). The latter, defining so called or-groups, means that at least one sub-clafer must be instantiated. This captures a common pattern of a required subsystem, that has a number of variations, which can coexist; for instance, different compression algorithms or different authentication protocols in software applications.
More information: Tutorial: Group Cardinalities
If the group cardinality constraint is anything else than
0..*(which is the default one, corresponding to no restriction), then the default cardinality for each of the children is?(otherwise1as explained in the previous page). This is natural, as mandatory features do not make sense in groups with restricted cardinality – they would immediately produce an inconsistency in the model.Clafers can be arbitrarily nested. Thus our mandatory clafers (first level of nesting) still are mandatory, but their subclafers are optional.
More information: Tutorial: Cardinality
How many model instances are possible now?
Let’s use another tool, ClaferConfigurator, to generate
all instances.
Task 2:
Press the button to open the model from this page in the configurator and press the button
Runin theInstance Generatorwindow – it will try to generate 10 instances. Make sure that you are using an Alloy based generator, not the choco and not the Z3 based.The green tick
 indicates
the presence of a clafer in a given instance, the red crossed circle
indicates
the presence of a clafer in a given instance, the red crossed circle
 its absence. All
mandatory clafers are also present in every instance as indicated by
gray checked checkboxes
its absence. All
mandatory clafers are also present in every instance as indicated by
gray checked checkboxes  in the left column.
in the left column.Note that, in general, making a clafer mandatory does not guarantee that it will be present in all instances, since it can be a child of an optional clafer.
Close the configurator
For completeness we include the same model in the popular FODA [FODA] notation:
Clafer also has a simple visualization tool translating models to the VSpec notation of Common Variability Language (CVL). This is very similar to FODA feature models:
- Move to the page
 Do not
Repeat Yourself.
Do not
Repeat Yourself.
Previous
